
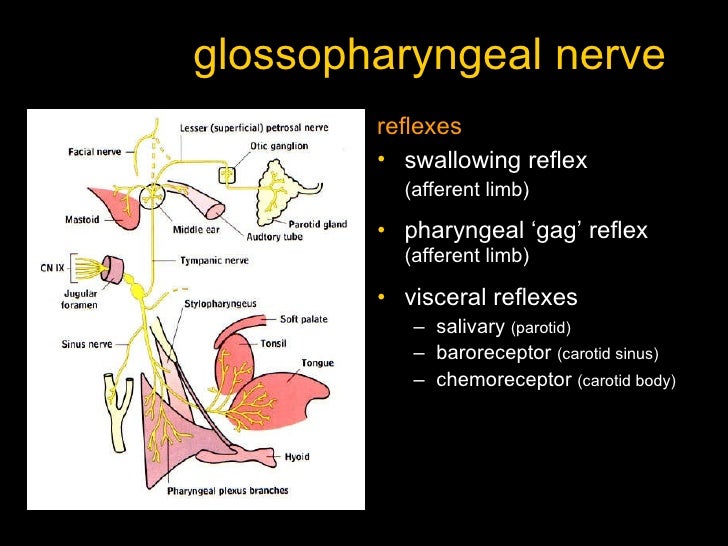
Here, it forms the tympanic plexus – a network of nerves that provide sensory innervation to the middle ear, internal surface of the tympanic membrane and Eustachian tube.Īt the level of the stylopharyngeus, the carotid sinus nerve arises. It penetrates the temporal bone and enters the cavity of the middle ear. The tympanic nerve arises as the nerve traverses the jugular foramen. The glossopharyngeal nerve provides sensory innervation a variety of structures in the head and neck.

The nerve enters the pharynx by passing between the superior and middle pharyngeal constrictors. Within the pharynx, it terminates by dividing into several branches – lingual, tonsil and pharyngeal. It also gives rise to the carotid sinus nerve, which provides sensation to the carotid sinus and body. At the inferior margin of the stylopharyngeus, several branches arise to provide motor innervation to the muscle. Now extracranial, the glossopharyngeal nerve descends down the neck, anterolateral to the internal carotid artery. They are known as the superior and inferior (or petrous) ganglia – they contain the cell bodies of the sensory fibres in the glossopharyngeal nerve. Immediately outside the jugular foramen lie two ganglia (collections of nerve cell bodies). It has a mixed sensory and parasympathetic composition. At this point, the tympanic nerve arises. The nerve leaves the cranium via the jugular foramen.

It emerges from the anterior aspect of the medulla, moving laterally in the posterior cranial fossa. The glossopharyngeal nerve originates in the medulla oblongata of the brain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
